How to Choose a Secure Crypto Wallet: A Comprehensive Guide for 2026
Learn how to choose a secure crypto wallet in 2026. Compare hardware, software, hot & cold wallets. Expert security tips, wallet features & best practices for protecting digital assets.
Selecting a secure cryptocurrency wallet is one of the most critical decisions in your crypto journey. With over $1.4 trillion in total cryptocurrency market capitalization and evolving security threats, understanding the nuances of wallet selection is essential to protect your digital assets. This guide walks you through the key factors to consider when choosing a crypto wallet that aligns with your security needs, usage patterns, and investment strategy.
Understanding Crypto Wallets and Their Purpose
A cryptocurrency wallet is a digital tool that stores your private and public keys, enabling you to send, receive, and manage your digital assets. Unlike traditional bank accounts, crypto wallets give you direct control over your funds—but this power comes with responsibility. Your private keys are cryptographic codes that unlock access to your cryptocurrency. If someone obtains your private keys, they can steal your funds immediately, and there's often no recovery mechanism.
The fundamental security principle in cryptocurrency is straightforward: whoever controls the private keys controls the funds. This is why choosing the right wallet and managing it properly is non-negotiable.
Hot Wallets vs. Cold Wallets: The First Critical Choice
The first decision in wallet selection is determining whether you need a hot wallet (connected to the internet) or a cold wallet (offline storage).
Hot Wallets: Convenience with Higher Risk
Hot wallets are software-based solutions that remain connected to the internet. They include mobile apps, desktop applications, and browser extensions. Hot wallets are ideal for frequent traders and users who need quick access to their funds for regular transactions.
Advantages:
- Immediate access to funds for trading or transactions
- User-friendly interfaces designed for quick operations
- Support for multiple cryptocurrencies and blockchain networks
- Easy integration with decentralized finance (DeFi) applications and NFT marketplaces
Security Concerns:
Hot wallets remain connected to the internet, making them susceptible to malware, phishing attacks, and keylogger infections. If your device is compromised, attackers can potentially access your private keys. For this reason, security experts recommend limiting the amount of cryptocurrency stored in hot wallets to only what you need for regular transactions—typically no more than 5-10% of your total portfolio.
Cold Wallets: Maximum Security for Long-Term Storage
Cold wallets store your private keys offline on a physical device or paper, completely disconnected from the internet. Hardware wallets like Ledger, Trezor, and SafePal are the most popular cold storage solutions.
Advantages:
- Private keys remain offline, immune to online attacks and malware
- Physical confirmation buttons for transaction signing prevent unauthorized transfers
- Protection against remote hacking and phishing attacks
- Recovery seed phrases allow fund restoration if the device is lost
- Support for thousands of cryptocurrencies
Limitations:
- Less convenient for frequent trading or DeFi interactions
- Requires physical device purchase (typically $50-300)
- Steeper learning curve for beginners
- Risk of physical loss or damage (though seed phrases provide recovery options)
Industry consensus suggests that security-conscious investors use a hybrid strategy: cold wallets for storing the majority of assets (80-95%) and hot wallets for active trading and DeFi participation.
Custodial vs. Non-Custodial Wallets: The Control Question
Your choice of wallet also determines who controls your private keys—you or a third party.
Non-Custodial Wallets: You Control Your Keys
In non-custodial wallets, you are the sole custodian of your private keys and funds. No third party manages, holds, or has access to your crypto. Examples include MetaMask, Trust Wallet, Exodus, and hardware wallets.
Advantages:
- True ownership and control of your assets
- No withdrawal limits or transaction delays
- Protection from exchange failures or platform insolvencies
- Faster transactions without intermediaries
- Lower fees due to no custodial charges
Disadvantages:
- You bear full responsibility for security and loss prevention
- No password recovery if you forget your credentials
- No insurance coverage for theft or loss
- Requires active management and security practices
Custodial Wallets: Third-Party Management
Custodial wallets are offered by cryptocurrency exchanges and platforms like Coinbase Wallet and Crypto.com, where the provider manages your private keys on your behalf.
Advantages:
- Simplified user experience—no need to manage private keys
- Password recovery options if credentials are forgotten
- Insurance protection against theft or platform breaches
- Customer support available for account issues
- KYC (Know Your Customer) compliance for regulatory purposes
Disadvantages:
- You don't control your private keys—the platform does
- Vulnerability to exchange hacks (the $90 million Liquid Exchange hack is a cautionary example)
- Potential for fund freezes or withdrawal restrictions
- Higher fees due to custodial services
- Risk of platform insolvency affecting your assets
For serious crypto investors, non-custodial wallets are generally recommended because they align with cryptocurrency's core principle of self-sovereignty and eliminate counterparty risk.
Key Security Features to Evaluate
When assessing wallet options, examine these critical security components:
Private Key Generation and Storage
The wallet must use cryptographically secure random number generators (RNGs) for private key creation. Hardware wallets generate keys completely offline, ensuring they're never exposed to the internet. Verify that the wallet uses industry-standard cryptography protocols and avoid wallets with unproven security models.
Secure Element Chip
Premium hardware wallets include a certified secure element chip (typically EAL6+ certified—the same security level used in passports). This tamper-resistant component stores private keys and prevents physical attacks even if someone physically accesses the device.
Two-Factor Authentication (2FA)
Enable 2FA on all wallet accounts. Authenticator apps like Google Authenticator, Authy, or Aegis are more secure than SMS-based 2FA, which is vulnerable to SIM swapping attacks. For high-value accounts, consider hardware security keys like Ledger Stax or YubiKey that require physical verification.
Transaction Signing Verification
The best hardware wallets display transaction details on a dedicated secure screen before signing. This prevents "transaction substitution" attacks where malware attempts to redirect your cryptocurrency to attacker addresses. Always verify the recipient address and transaction amount on the wallet's own screen.
Multi-Signature Wallets
Multi-signature (multisig) technology requires multiple private keys to authorize a transaction—for example, a 2-of-3 or 3-of-5 setup. This is particularly valuable for institutional investors, joint accounts, or holders of large cryptocurrency amounts. Platforms like Casa and Nunchuk specialize in multisig wallet management.
Biometric Authentication
Modern wallets increasingly integrate fingerprint recognition and facial authentication, adding a biometric layer of security on mobile devices. Ensure these are implemented securely through the device's secure enclave (iOS) or Strongbox (Android).
Third-Party Security Audits and Certifications
Professional security audits provide critical assurance about a wallet's implementation. Look for wallets that have undergone independent security assessments:
- CertiK Skynet Score: A real-time evaluation system providing independent assessments of Web3 projects, exchanges, and wallets. Many leading wallets display their Skynet scores on their platforms.
- Professional Audit Firms: Respected security firms like Trail of Bits, OpenZeppelin, Certora, Kudelski Security, and Riscure conduct comprehensive wallet audits.
- Audit Scope: Examine what was audited—ideally, assessments should cover private key generation, cryptographic implementation, transaction signing security, and protection against malware and phishing attacks.
Wallets that have undergone multiple independent audits and passed third-party security reviews demonstrate a commitment to user protection. However, no audit guarantees complete immunity from all threats—security is an ongoing process.
Evaluating Popular Wallet Options
Ledger Nano Flex and Nano X (Hardware Wallets)
Security Rating: AAA (CertiK Skynet Score: 86.26)
Best For: Long-term storage, institutional investors, maximum security
- Supports 5,500+ cryptocurrencies and tokens
- EAL6+ certified secure element chip
- Bluetooth connectivity for mobile management
- 2.84" touchscreen for easy transaction verification
- Built-in staking support for 20+ networks
- Ledger Live software for portfolio management
Considerations: Requires Ledger Live app for full functionality; Bluetooth connectivity introduces slightly more attack vectors than air-gapped devices.
Trezor Safe 3 and Safe 5 (Hardware Wallets)
Security Rating: C (for Safe 3, hardware is excellent but software support varies)
Best For: Bitcoin enthusiasts, privacy-focused users, those valuing open-source code
- Completely open-source design and firmware
- Advanced Shamir backup for distributed recovery
- Optional passphrase protection
- Touchscreen for secure PIN entry
- Strong privacy features including Tor integration
- No support for Cardano and some altcoins
Considerations: Less extensive cryptocurrency support than Ledger; active community required for technical support.
MetaMask (Hot Wallet)
Security Rating: AAA (CertiK Skynet Score: High)
Best For: DeFi users, NFT collectors, Ethereum ecosystem
- De facto standard for Web3 interactions
- Seamless integration with decentralized finance apps
- Strong NFT marketplace integration
- Hardware wallet compatibility for enhanced security
- Customizable transaction settings and slippage controls
- Available across browsers and mobile
Considerations: Connected to the internet—best used with small amounts or integrated with hardware wallets.
Zengo (Hot Wallet)
Security Rating: AAA (CertiK Skynet Score: 85.29)
Best For: Cryptocurrency beginners, users seeking simplified security
- Eliminates complex seed phrases using multi-party computation (MPC) technology
- Keyless security model—recovery via biometric or email
- 24/7 live customer support
- Intuitive, user-friendly interface
- Supported on Android, iOS, Linux, Mac, Windows
Considerations: Lower number of supported cryptocurrency networks compared to competitors; higher in-app exchange fees.
Exodus (Hot Wallet)
Security Rating: AAA (CertiK Skynet Score: 85.42)
Best For: Beginners and intermediate users, multi-asset management
- Support for 50+ blockchain networks
- Native integration with Trezor hardware wallets
- Built-in crypto swapping
- Clean, intuitive interface
- Desktop and mobile versions
Considerations: Limited transparency regarding security audits; centralized control over transaction fees.
SafePal S1 (Hardware Wallet)
Security Rating: High with air-gapped design
Best For: Budget-conscious buyers, hybrid mobile-hardware wallet users
- Air-gapped QR code signing (no cables or Bluetooth)
- Supports 100+ blockchains
- DeFi-ready with mobile app integration
- Affordable price point
- Self-destruct protection against tampering
Considerations: Smaller screen than premium options; less extensive feature set.
Tangem (Card-Style Hardware Wallet)
Security Rating: EAL6+ certified secure element
Best For: Portability, simplicity, non-technical users
- Credit card-sized NFC-powered hardware
- No battery or cables required
- Seedless design—cards are tied to wallet security
- Extremely portable
- Supports many blockchains
Considerations: Requires NFC-enabled phone; replace cards rather than restore.
The Decision Framework: Choosing Your Wallet
Use this structured approach to select the ideal wallet for your situation:
Step 1: Assess Your Usage Patterns
- Frequent Trading: Use hot wallets like MetaMask or Exodus
- Long-Term Holding: Use cold wallets like Ledger or Trezor
- Mixed Strategy: Combine both—80-95% in cold storage, 5-20% in hot wallets
Step 2: Determine Your Risk Tolerance and Holdings
- Beginner/Small Holdings: Zengo or Coinbase Wallet for simplicity
- Experienced/Moderate Holdings: Exodus, Trust Wallet, or Ledger Nano
- Advanced/Large Holdings: Trezor Model T, Ledger Flex, or multi-signature setups
Step 3: Identify Cryptocurrency Requirements
List the specific coins and tokens you hold. Verify that your chosen wallet supports each asset. Some wallets focus on specific blockchains (e.g., Bitcoin-only wallets), while others support thousands of tokens.
Step 4: Evaluate Security Features
Prioritize wallets with:
- Third-party security audits
- Secure element chips (for hardware wallets)
- Multi-factor authentication options
- Open-source code (if you're technically proficient)
- Regular firmware/software updates
- Established track records with minimal security incidents
Step 5: Check Custody Model
- Prefer non-custodial wallets for maximum control
- Accept custodial wallets only from reputable, regulated platforms with insurance
- Never use an unproven or new platform for significant holdings
Step 6: Verify Interface and Usability
Test the wallet's user interface before committing substantial funds. A wallet is only secure if you'll actually use it correctly. Poor usability often leads to security mistakes.
Essential Security Practices for Wallet Management
Selecting the right wallet is only half the battle. Your behavior determines whether that wallet remains secure:
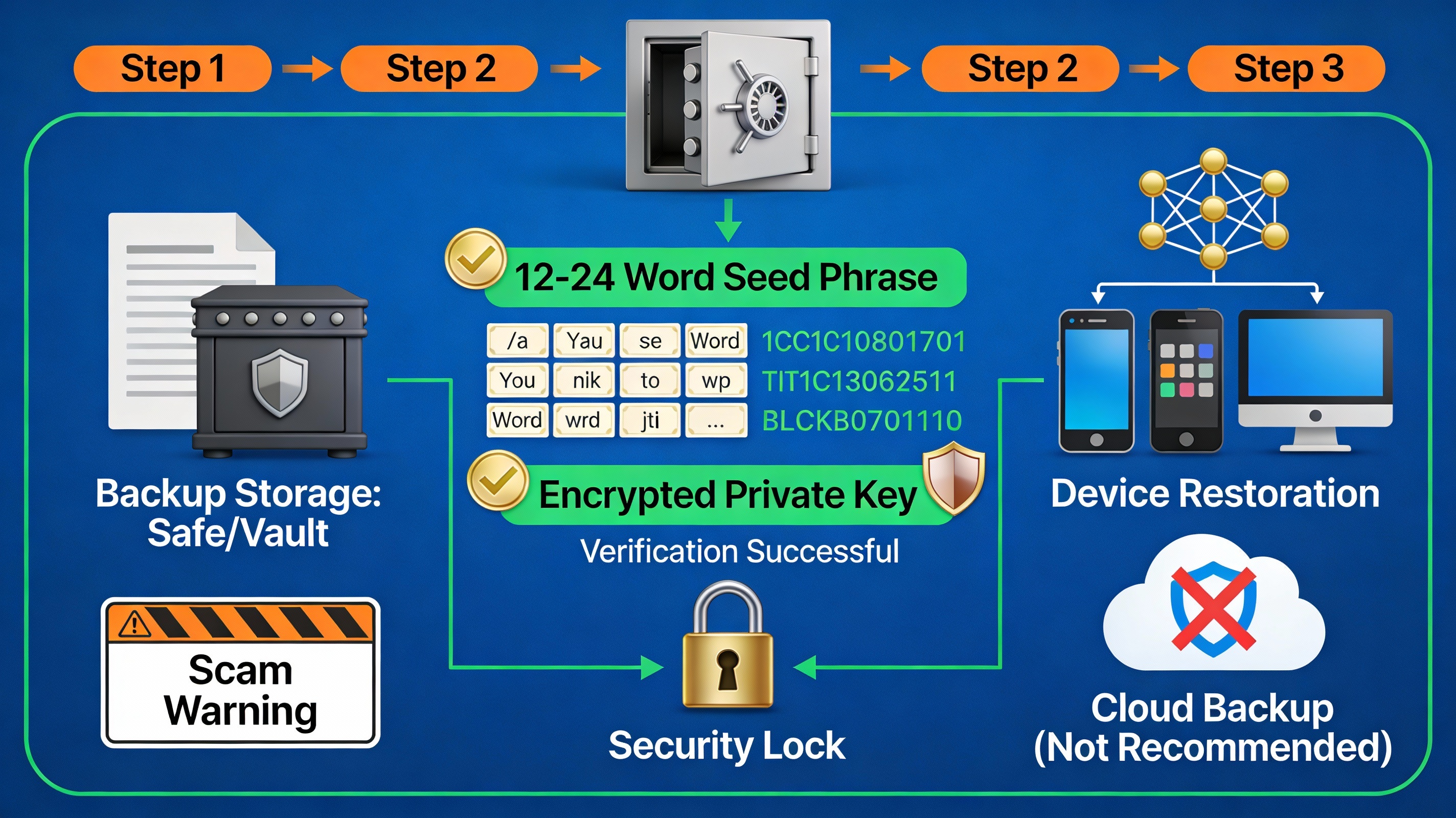
Seed Phrase Management: Your Most Critical Asset
Your seed phrase (12 or 24 words) is the master key to your cryptocurrency. If someone obtains it, they control your funds permanently.
Secure Backup Methods:
- Metal Seed Plates: Etch your seed phrase onto titanium or steel plates (fireproof, waterproof, corrosion-resistant). Products like Cryptotag and CryptoSteel are industry standards.
- Offline Storage: Store a written copy in a secure, offline location like a safe, safety deposit box, or secure home safe—separate from your hardware wallet.
- Shamir's Secret Sharing: Advanced users can split seed phrases into multiple shards, distributing them across trusted locations so no single theft exposes your wallet.
- Digital Vault Services: Vault12 and Casa offer decentralized backup solutions using encrypted shards and trusted "Guardians."
Critical Rules:
- Never store seed phrases digitally (no screenshots, notes, or cloud storage)
- Never photograph your seed phrase
- Never share your seed phrase with anyone—not even wallet providers or support staff
- Always store backup copies in multiple secure locations
Multi-Factor Authentication on All Accounts
Enable 2FA on your wallet accounts and connected exchanges. Use authenticator apps rather than SMS when possible. For large holdings, add hardware security keys.
Regular Software and Firmware Updates
Outdated wallet software exposes you to known vulnerabilities. Set automatic updates when available, and manually check manufacturer websites monthly for hardware wallet firmware updates. Always download updates directly from official sources, never from third-party links.
Avoid Public Wi-Fi for Sensitive Transactions
Public networks are vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks. For significant transactions, use a secure VPN with strong encryption or limit wallet activity to trusted private networks.
Separate Wallets for Different Purposes
- Cold Wallet: Long-term storage of core holdings
- Hot Wallet: Daily trading and DeFi interactions
- Risky Activities Wallet: Separate wallet for testing new protocols, yield farming, or speculative ventures
This compartmentalization limits damage if one wallet is compromised.
Verify Addresses Before Transactions
Before sending cryptocurrency, always verify the recipient address on your wallet's secure screen (for hardware wallets) or by double-checking manually. Clipboard hijacking malware can substitute addresses. Never copy-paste addresses blindly.
Beware of Common Attack Vectors
Phishing Attacks: Scammers create fake wallet websites and emails requesting seed phrases or login credentials. Always verify the URL before entering sensitive information.
Malware and Keyloggers: Install antivirus and anti-malware software. Avoid downloading unverified applications or clicking suspicious links.
Supply Chain Attacks: Purchase hardware wallets directly from official retailers or authorized distributors. Counterfeit devices exist in secondary markets.
Social Engineering: No legitimate company will ask for your seed phrase or private keys. Never disclose these under any circumstances.
Common Mistakes to Avoid
- Storing seed phrases digitally: The most frequent security failure. Digital storage is permanently vulnerable to hackers.
- Using weak or recycled passwords: Strong, unique passwords are essential. Use a password manager like 1Password, Bitwarden, or KeePass.
- Neglecting firmware updates: Outdated firmware leaves known vulnerabilities unpatched.
- Mixing trading with long-term storage: Using your main wallet for risky transactions increases overall exposure.
- Failing to test recovery procedures: Verify that you can recover funds using your seed phrase before storing significant amounts.
- Trusting fake wallet applications: Always download from official sources. Research wallet reviews on trusted forums.
- Ignoring security audit reports: Third-party audit findings reveal critical vulnerabilities. Favor audited wallets over untested alternatives.
Security for Different User Types
Cryptocurrency Beginners
Start with Zengo or Coinbase Wallet for simplified experience, then graduate to a hardware wallet like Ledger Nano S Plus or Trezor Safe 3 once comfortable. Keep holdings modest until you master wallet management.
Active Traders
Use a combination of MetaMask or Trust Wallet for frequent trading/DeFi, connected to a hardware wallet for enhanced security. Maintain most holdings in cold storage.
Long-Term Investors ("Hodlers")
Purchase a Ledger Nano Flex or Trezor Safe 5 for maximum security. Store seed phrases in multiple physical locations. Enable all available security features and update firmware regularly.
Institutional/Large Holdings
Consider multi-signature solutions through platforms like Casa, Unchained, or Nunchuk. Distribute keys across multiple team members or locations. Combine with institutional custodians for additional security layers if preferred.
The Future of Wallet Security
Wallet technology continues to evolve with emerging security innovations:
- Quantum-Resistant Cryptography: Development of encryption methods resistant to future quantum computing threats
- Zero-Knowledge Proofs (ZKPs): Verification of transactions without exposing sensitive data
- Decentralized Identity (DID): User-controlled identity management reducing reliance on centralized servers
- AI-Powered Threat Detection: Real-time monitoring and anomaly detection to identify suspicious activity
Stay informed about these developments as wallet security continues advancing.
Security Through Informed Choices
Choosing a secure crypto wallet requires evaluating multiple factors—custody type, storage method, security features, audit history, and your specific use case. There is no single "best" wallet for everyone; the optimal choice depends on your circumstances.
The fundamental principle remains constant: only use wallets from established, audited providers; maintain complete control of your private keys and seed phrases; implement multi-factor authentication; and follow security best practices consistently. The cost of cryptocurrency security is measured in time and attention, not in financial expense. Taking these steps protects your digital assets from the majority of attack vectors.
Your cryptocurrency is only as secure as your weakest link—be that weak link as strong as possible through informed wallet selection and disciplined security practices.
Comments 0
Most Read
What Is the Concept of Tokenization in Blockchain?
Bitcoin & Ethereum Market Momentum Update
Recommended Post
What Is the Concept of Tokenization in Blockchain?
How Do I Avoid Common Mistakes When Trading Cryptocurrencies?
How Do I Recover a Lost Cryptocurrency Wallet?
How Can I Learn More About Cryptocurrency and Blockchain Technology?
How Do I Track Cryptocurrency Prices in Real-Time?







Leave a Comment